uPDATE wp5 - Performance prediction
Quantification of the effect of preventive interventions on the ingress of chloride into concrete structures
Chloride ingress is a common issue in concrete structures that can result in reinforcement corrosion. In order to extend the lifetime of a structure, several preventive repair methodologies are available, which reduce the ingress of chlorides. In this work, the computational efficiency of the analytical model for a two-material diffusion problem has been improved to model the effect of a mortar overlay or partial cover replacement, and is further implemented to model the influence of a coating. This enables the assessment of each repair method in a probabilistic framework using Latin hypercube samples within an acceptable timeframe. A parameter study executed in both a deterministic and probabilistic framework demonstrated the model efficiency and the importance of the timing and quality of the intervention for successful repair when applying a repair intervention in the initiation phase.
For further reference is referred to https://doi.org/10.1002/suco.202300784.
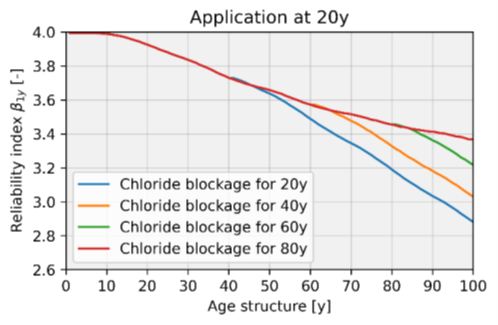
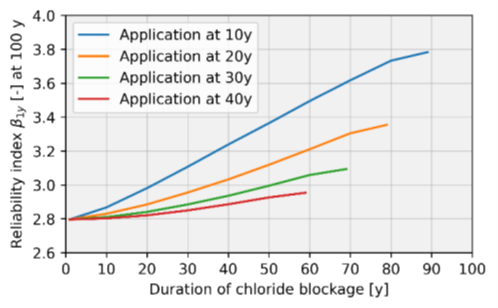
An alternative approach is to model the coating as impermeable but with a limited service life. By application of the chloride blockage, the deterioration of the concrete structure can be delayed and thus the reliability index (β) can be increased compared to a situation without intervention. The influence of the application time and blockage duration has been investigated. For further reference is referred to the proceedings of IABMAS 2024.
K. Van Den Hende et . al., Influence of repair interventions on the safety of a reinforced concrete road bridge subjected to chloride ingress, Proc. IABMAS24, 24-28 June 2024, Copenhagen, Denmark
Evaluation of bending capacity of prestressed concrete elements subjected to corrosion
At the moment, an algorithm is being developed to accurately quantify the bending moment capacity for an existing prestressed (pre- or post-tensioned) concrete structure subjected to corrosion. This algorithm is linked with the chloride ingress modelling over time to predict the safety of an element over time. This allows to objectively compare the effect of different intervention types and enables one to choose the most appropriate solution for each specific case. For further reference is referred to the proceedings of fib 2024 (to be published).
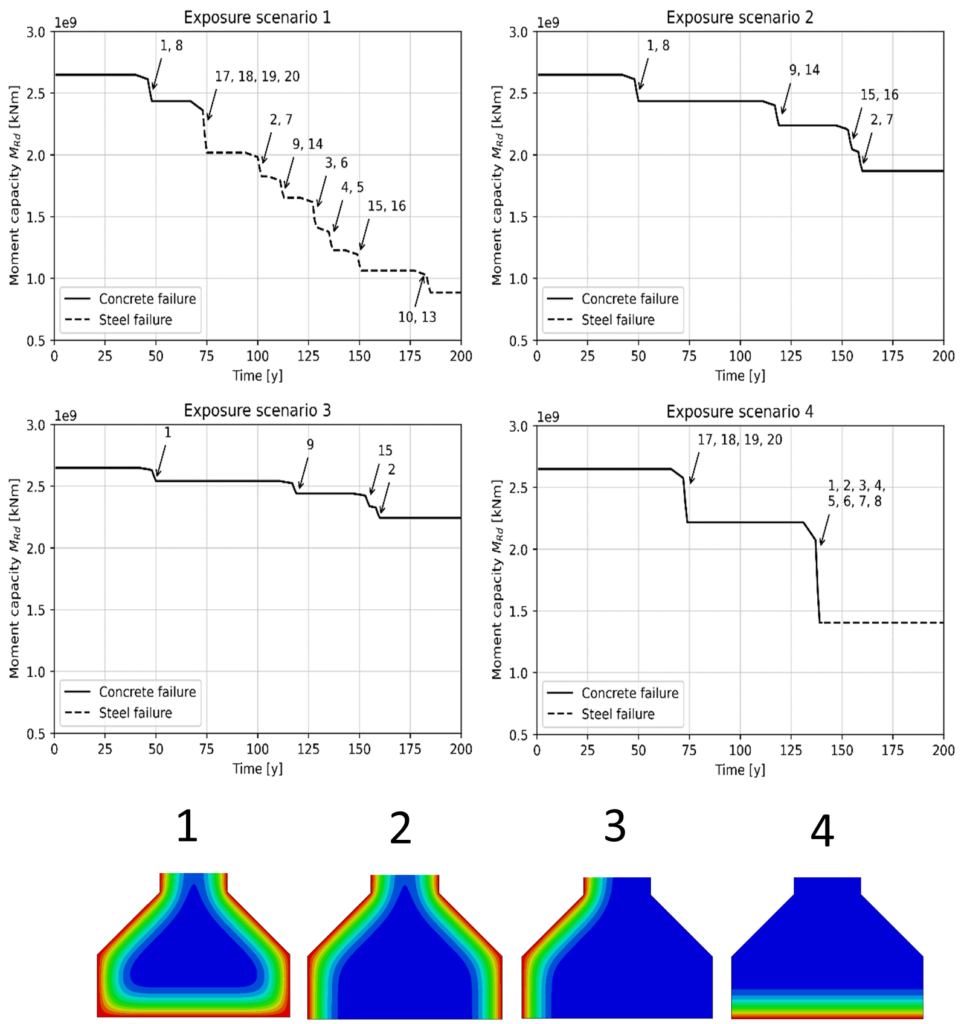
Van Den Hende et al., Quantifying the influence of chloride-induced corrosion on the bending moment capacity of a prestressed girder considering different exposure scenarios, Proc. fib Symposium 2024, 11-13 November 2024, Christchurch, New Zealand